PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.15% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
|
|
|
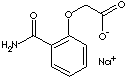
| SODIUM (2-CARBAMOYLPHENOXY)ACETATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 3785-32-8 |
|
| EC NO. | 223-249-9 | |
| FORMULA | H2NCOC6H4OCH2COONa | |
| MOL WT. | 217.16 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Salicylamide O-acetate sodium salt; | |
| (2-Carbamoylphenoxy)acetic acid sodium salt; Natrium-[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenoxy]acetat; [2-(Aminocarbonil)fenoxi]acetato de sodio; [2-(aminocarbonyl)phénoxy]acétate de sodium; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Salicylic Acid is a white crystalline powder or needle-shaped crystals with sweetish taste; soluble in acetone, ether, alcohol, boiling water, benzene and turpentine, sparingly soluble in chloroformbenzene, slightly soluble in water; melts at 158 C. It is prepared commercially by sodium salicylate which derived from sodium phenolate with carbon dioxide under heating and pressure. It contains both a hydroxyl and a carboxyl group, which react with either an acid or an alcohol. The carboxyl group forms esters with alcohols; e.g. methyl salicylate is formed with methanol, which used in food flavorings and preservatives; menthyl salicylate is formed with methanol, which is used in suntan lotions; phenyl salicylate (called salol) is formed with phenol, which is used as an antiseptic and antipyretic agent. The hydroxyl group reacts with acetic acid to form acetylsalicylic acid (called aspirin). Salicylic Acid is important for the preparation of other pharmaceutical products, dyes, flavours, and preservatives. The sodium salt (Sodium salicylate), a shiny white powder, is used for antiseptics preparations and as a preservative. Salicylic Acid derivatives are used in formulating flavors, preservatives and UV absorbers for food and cosmetics as well as plastics. They are used in manufacturing pharmaceuticals mainly analgestics and antipyretics for the relief of pain and fever. Salicylamide, amide of salicylic acid, is used as an analgesic, antipyretic, and antirheumatic drug as well as fungicide. It is also used in manufacturing mordant dyes. Carbamic acid is a compound of chemical formula H2NCOOH. But it exists only in the form of carbamate (its salt or ester), carbamide (amide) and carbamoyl (acyl radical). Carbamates , with general formula -NH(CO)O-, have functional groups next to the carbonyl group. Carbamate is formed when a carbon dioxide reacts with the amino group the COO- group is a resonance structure. Carbamate structure inhibits cholinesterase and many insecticides and parasiticides contain carbamate fuctional group. Carbamate is a poisonous ingredient in insecticide. Other common examples of poisonous ingredients in insecticide include organophosphates and dichlorobenzenes. It is highly toxic to human also. Heavy exposure to IT can cause carbamate poisoning. Natural carbamide (urea) can be found in protein metabolism in urine. Carbamoyl is the radical NH2CO-, also called carbamyl. It is a radical formed from an organic acid by removal of a hydroxyl group. It is involved in the biosynthesis of the pyrimidine ring. Carbamoyl compounds, such as salicylamides, are important for the preparation of pharmaceutical products, pesticides, dyes, and biosynthesis researches. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder | |
| ASSAY | 98.0 - 101.0% | |
| WATER | 2.0% max | |
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.15% max |
|
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: | ||
|
|
|